PSSH is a program used for executing the SSH in parallel on several hosts. It has the features of sending the input to all processes, transferring the password to SSH, saving the output files, and managing the time out. Parallel SSH or PSSH enables users to execute the commands on multiple hosts parallelly.
Users can increase their productivity with the aid of this powerful tool. Some of the most important functionalities of the PSSH include sending input to all of the processes, inputting a password to SSH, saving the output to files, sysadmin task automation such as patching servers or looking for error logs.
For you to execute a simple command in multiple nodes or gather data from multiple sources; you need to log in to every node and collect the data manually. PSSH lets you perform this task with the help of just a single command.
Why Users want PSSH Alternatives?
PSSH is an amazing all-in-one software tool for parallel command execution on multiple hosts simultaneously. Users who want to achieve the advanced execution of remote commands executable on multiple hosts and do not want the hectic tasks of managing the servers can try more robust alternatives.
On the other hand, it is very hard to achieve such impressive feats using other software that requires manual data manipulation. Depending on the type of tasks users are doing with the help of the alternative tool, i.e., deleting or editing files, they always have to count on some hurdles that you may face.
Users tend to select the other software tool instead of PSSH for complex operations, and they mostly prefer the PSSH for only status queries. If someone wants to test out the changes to their programs in a testing environment before sending the files to the production servers, they might opt for alternative tools.
List of PSSH Alternatives
Based on the functionalities of different software tools and the potential setbacks for the PSSH tool, a list of the best fourteen tools has been compiled for parallel execution of commands on multiple hosts. Some superior software to PSSH supports the execution of commands via sudo.
One task that is mostly not well handled well in SSH is keeping a complete check on multiple hosts behind a gateway host, which requires one to connect first to the gateway and then port forwarding from there on to proceed further.
Some of the tools listed here can also be written according to users’ needs if they have expertise in python language, which is quite a feat to perform such an incredible task with the flexibility of execution of your own customized program.
1. OpenSSH
OpenSSH is one of the best and frequently used power tools for Linux, well known for ensuring secure connections to the remote Linux system through a shell and letting you share the files through and to the remote systems securely and efficiently.

It is compatible with all SSH protocols and provides additional secure tunneling capabilities, state-of-the-art configuration options, and numerous authentication methods. It has the best features that support data security, data encryption, data management, and the best peer-to-peer communications.
However, the largest setback of this tool is that you are unable to execute the same command simultaneously on multiple hosts in one attempt as it is not designed to handle such tasks. OpenSSH provides the best defense against cyberattacks, eavesdropping, and connection hijacking by encrypting the traffic data.
Features
- Sensitive Data Compliance
- Data Transport
- Data Security
- API Integration
Pros
- Secure Data Handling
- Clean File-Based Architecture
- Simple to Use
Cons
- Slow Communication with Servers
- Single Developer Issue
2. PuTTY
PuTTY is a free, open-source terminal application with the best configurable features. In addition to the basic features of serial terminal communications, telnet, SSH, rlogin, and so on. It can also secure file transfers with the help of SFTP and SCP.
It is able to operate as an SSH tunnel for X11 traffic. The tool is best suitable for administrators, network engineers, IT professionals, and developers who connect to the remort systems. PuTTY fixed several problems by filling the technology gap created by Microsoft Windows when it stopped shipping with HyperTerminal.
Features
- Unicode Support
- SSH Encryption Keys
- Control over Port Forwarding
- Resource Usage
- Latency
Pros
- Ease of Use
- Best Remote Features
- Easy to Configure
- Linux Console Sequence
Cons
- No Copy and Paste Option
- Complex Non-text Files Transfer
3. Ansible
Ansible is an open-source automation software, or tool, used for IT tasks such as application deployment, configuration management, provisioning, and interservice orchestration. It provides automation for Unix-like systems and can also configure the Microsft Windows.
Automation is very important as administrators and developers have to keep up with too complex IT environments, often needing them to scale too quickly for the system if they have to do everything manually. Sensitive data can be secured with the help of Ansible.
Automation simplifies complex tasks, making developers’ jobs more manageable and giving them the freedom to focus their most undivided attention on other important goals that optimize organizational productivity. In other words, it provides spare time and increases efficiency.
Features
- Configuration Management
- Application Deployment
- Orchestration
- Cloud Provisioning
Pros
- Free Open Source
- Easy to Use
- Powerful and Flexible Tool
- Agentless
Cons
- Less Interactive UI
- No Notion of State
- Minimal Support
4. FAI
Fully Automatic Installation is a non-interactional system to install a DebianGNU operating system unaccompanied on single, numerous computers or a whole cluster simultaneously. It is an ideal tool for migrating your system now and then as you desire from one hardware to another.
FAI is a manageable tool for system updates, and provides you with the same configuration of initial installation and then installing the updates. It is used for maintaining chroot environments, virtual machines, and physical boxes in setups ranging from a few single systems to several thousands of systems.
You can easily establish different configuration requirements on different hardware with the help of it, and you do not have to repeat the information that has already been shared with various machines. FAI allows you to tune every small detail of your configuration to your requirements with the help of hooks.
Features
- Fully Automated Installation
- Performs Softupdates
- Automatic Hardware Detection
- Diskless Client Support
Pros
- Ease of Use
- Flexible System
- Fast to Deploy
Cons
- Boot Errors
- Installation is Cumbersome
5. ConEmu
ConEmu, also known as ConEmu-Maximums5, is an advanced console window. it is an open-source project, and you can run it on Microsoft Windows. ConEmu operates as the terminal for “console” type applications and a sort of conscript environment for GUI execution and it was primarily built as a Far Manager companion.
Still, you can use ConEmu with other console and GUI apps that run on Windows, such as PowerShell, bash, PuTTY, Notepad, and numerous more applications. Although it is a progressive console and not a shell, you can even run any shell you want, and it has an extensive list of features.
Features
- DosBox Integration
- Customize Starting Tabs
- Graphic Windows Models
- Run Simple GUI Apps
- Thumbnails and Titles
Pros
- Use Different Windows Fonts
- Support for 24-bit Colors
- Deep Integration
- User-Friendly Interface
Cons
- Only for Windows
- Sometimes Hard to Understand
6. pconsole
pconsole is the parallel console tool utilized as an interactional, managerial shell software tool for clusters. It provides you the freedom to connect to each node of your cluster simultaneously. Its utility generates a host terminal window for each remote host specified on the command line.
You can type your administrative commands in a specialized window that ‘multiplies’ the input to each connection you have accessed recently. pconsole is best run from within X Windows, although it is possible to employ it without X, in console mode.
The utility also features a central, or master, console window that broadcasts what you input to each connection you open. You need to install pconsole on only one machine in the cluster, and this would usually be your central administrative mode.
Features
- Administrative Tool
- Parallel Access to Multiple Machines
- Secure Access
Pros
- Simple User Interface
- Secure Programm
- Easy Installation
Cons
- Not Better Option for non-SSH
- Need Superuser Permission
7. (R)? ex
(R)? ex is a tool that can manage all your boxes from a central point. The tool is a stand-alone executable application for a single command or multiple tasks. Tasks are identified on the command line and are set out in Rex files. A Rexfile executes a similar task for remote execution as a Makefile performs for application installation.
It is defined through a small DSL but is specifically a Perl script that can be a constituent of random Perl as well. It arises from a parallel remote execution application with flexible software deployment and configuration management capabilities.
For code reuse, configuration instructions are placed in modules that a Rexfile can include. A template system for the layout of files is available. Unsatisfied with available implementations in 2010, the author of (R)? ex Jan Gehring decided to implement a Perl-based tool to cope with his requirements.
Features
- Process Automation
- Cross-platform Support
- Wide Packages
Pros
- Open Source
- Easy to Use
- Keep Configuration in Sync
Cons
- A Perl 5 Interpreter
- No SSH Disabling
8. KiTTY
KiTTY is a branch of PuTTY, the most established Telnet and SSH client for Windows and Unix. It functions on Windows, and it has an impressive collection of one of the most requested features missing from PuTTY. The tool has a very easy-to-use GUI with individual session icons and a config feature.
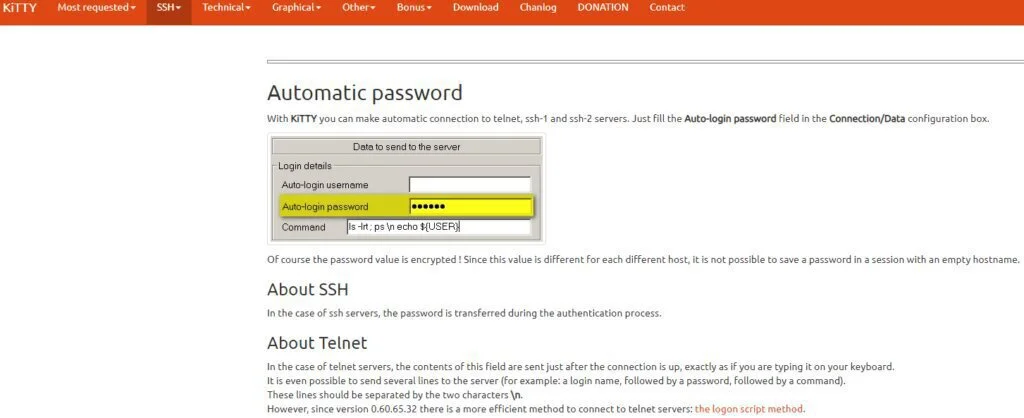
The app has various technical features, including running automatic commands, adding automatic passwords, and running locally saved scripts on remote sessions. It also has bonus choices, including a remote light chat server and a hidden text editor—all in all, a really useful client.
Features
- Sessions Filter
- Commands Portability
- Predefined Tools Shortcuts
- Session Launcher
- Automatic Login Script
Pros
- Predefined Commands
- Multiple PuTTY Sessions
Cons
- No Default Configuration
- No Central Configuration
9. Fabric SSH
Fabric is a high-level Python library generated to execute shell commands remotely over SSH, providing the best Python objects in return. Users need a remote host to better use Fabric SSH as the tool uses the Python programming language to create an SSH connection.
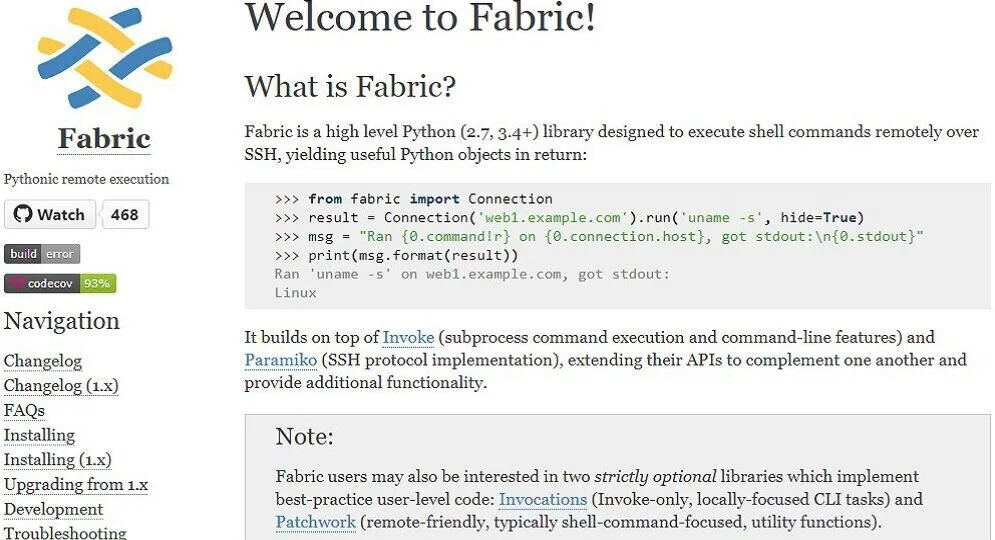
It interacts with SSH and computer systems to automate various tasks, from application distribution to general system administration. Although Fabric is Python-based, it does not mean that it is used strictly for working with other Python applications or tools.
It is the best tool for completing any task regardless of a specific language or a system. As long as the same basic needs are in order, you can benefit from this great library. Fabric manuscripts are based on basic Python executable files.
Features
- Serves Building
- Maintenance
- Monitoring
- Application Deployment
- Communication with Remote Host
Pros
- Automation Tasks
- Simple to Use and Maintain
- Agentless
- Single File Config
Cons
- Remote Host Password Specification
- No Answer to Complex Queries
10. Kadeploy
Kadeploy is an expandable, proficient, and reliable deployment system for cluster and grid enumerating. It provides a handful of tools for configuring, cloning, and managing cluster nodes. It can deploy up to a 300-nodes cluster in just minutes without interference from the system administrator.
It has an archive containing the operating system to deploy as input and copies it on the target nodes. As a result, the tool does not instate an operating system following a classical installation procedure. Rather users have to provide an archive of the operating system’s filesystem.
Kodeploy writes the PXE profiles on HTTP or TFTP servers to perform its installation task. It activates the reboot of computed nodes using SSH, IPMI, or a manageable PDU. The tool is best suitable for cluster and grid computing.
Features
- Minimal Environment Setup
- Application Deployment
- Reboot on Deployment Environment
- Management of Images
Pros
- Rights Management
- Statistical Collection
- Frontends to Low-Level Tools
Cons
- Available on Limited Platform
- Mishandling of Complex Scalability Tasks
11. MobaXterm
MobaXterm is the ultimate tool for remote computing tasks. It features numerous functions molded for IT administrators, programmers, web admins, and users who want to perform their remote jobs in the simplest way possible. There are many positive outcomes of equipping yourself with such an All-In-One network tool.
Graphical SFTP browser will automatically pop up to directly edit your remote files when you utilize SSH to connect to a remote server. Your remote applications will also be presented seamlessly on your Windows desktop using the embedded X server.
Features
- Tabbed Terminal
- Session Management
- Graphical SFTP Browser
- Multi Execution
Pros
- Unlimited Sessions
- Professional Support
- Master Password Support
Cons
- Occasionally Crashes
- Low-Quality Display
12. PontusVision
Pontus Vision is an open-source tool for data mapping and managing personal data. It helps companies follow data protection regulations, such as CCPA, LGPD, and GDPR. It helps provide structured and unstructured data. The Pontus Vision program is based on the POLE model used to perform the Track.
It helps measure the risk of the project being exposed to regulators’ diligence and minimizes the risks for unstructured data. It facilitates mapping all the data from the extract module, identifying the user with the help of as lesser data as possible, scalable to the trillion of the records.
The tool is a model used by the British Government to associate data with individuals. The POLE model creates relationships between People, Objects, Locations, and Events, forming the basis of a comprehensive and robust structure of data intelligence.
Features
- Structured Data Extraction
- Natural Graphical Reports
- DPIA Management
- Data Breach Analysis and Reports
Pros
- Custom Forms and Dashboards
- Consent Management
- Compliance Dashboard
Cons
- Complex Unstructured Data Handling
- Mismanagement of Scalability Tasks
13. GNOME Terminal
GNOME Terminal is terminal emulator software for retrieving a UNIX shell environment that can be utilized to run programs available on your system. Users can swiftly and easily take control of every single thing that goes on under the shiny surface of your Linux distro.
Terminal offers quick and accurate results for all commands you’d ever wish to use, and when implemented into bash scripts, allow you to repeat and even batch tasks too. You can save a lot of effort with the options that it provides.
Not in every terminal can you do shortcuts like renaming several files almost simultaneously and copying and pasting in the terminal, which saves users many writing sentences of characters for navigation. You can also utilize the same tools remotely from your machine.
Features
- Support Multiple Profiles
- Colored Text
- Mouse Events
- URL Detection
Pros
- Compatible with Older Software
- Allows Changing Background Color
- Text Rewarping and Resizing
Cons
- Require Commands to Interact
- Losses Last Progress
14. Cmder
Cmder is a software package built merely out of pure frustration over the absence of a usable console emulator on Windows. It is based on ConEmu with a major config overhaul, comes with a Monokai color scheme, amazing clink, and a custom prompt layout.
Cmdr is more of a software than a separate app, where all the magic happens with the help of ConEmu. You can get any operation with the help of a USB device or in the cloud storage; in this way, your history, storage, settings can be transferred to anywhere you like, and you don’t have to face the ugly Windows prompt ever again.
Features
- ConEmu Configuration
- Clink Supported
- Tab Manipulation
Pros
- Transfers Your Data Anywhere
- Custom Prompt Layout
Cons
- Not Available for Linux
Final Words
All the software tools discussed in detail are used for the secure connection of remote Linux systems with the help of secure shell hosting (SSH). The tools enable secure data transfer between two systems and simultaneously execute the commands on multiple hosts.
PSSH allows the parallel execution of commands on multiple hosts, which is very crucial as modern challenges require advanced security protocols. SSH is the best option for Linux to allow a secure connection between the SSH client’s two systems to connect to an SSH server.
Enterprises do not rely on passwords to authenticate privileged access to critical assets because of advancing hacking technologies. They have to adapt to the modern requirements of passwordless solutions of SSH-key-based authentication.